Swine flu 2016
“Swine flu” is a contagious acute infectious disease caused by pandemic influenza A (H1N1). The virus is transmitted by pigs and humans. The virus is characterized by fever, respiratory syndrome and severe with the possibility of death.
The swine flu virus was discovered in 1930 by Richard Shoup (United States). Within 50-60 years, the virus met and circulated only among pigs in North America and Mexico. Then swine flu was detected in humans, mostly pig farm workers, veterinarians.
We remember the last sensational swine flu epidemic in 2009 (the so-called California / 2009), which is emotionally and emphatically informed the population of the media. The epidemic is spreading from March 2009. The first cases of infection unknown strain of the virus have been reported in Mexico, followed by Canada and the United States. Swine flu spreads in 2016 in the United States, Canada, Mexico, Chilu, Britain, France, Germany, Australia, Russia, China, Japan and many others.
At the end of October 2016 according to the World Health Organization (WHO) laboratory confirmed: 537 248 cases of swine flu.
The highest sensitivity: among a group of people from 5 to 24 years. In second place: children up to 5 years.
During the 2016 epidemic virus assigned hazard class 6 (ie registration of the swine flu pandemic, which is easily transmitted from person to person and the disease seizes many countries and continents). According to official information the WHO cases of death at the end of the pandemic will be 17, 4 thousand people.
The causative agent of swine flu
There are several subtypes of the influenza virus in pigs (H1N1, H1N2, H3N2, H3N1). The ability to spread from person to person is only at H1N1. Influenza A (H1N1) – is the result of crossbreeding of human influenza A virus (H1N1) and swine influenza virus. As a result, the virus mutated and became the highly, and it’s called – pandemic virus. It is a pandemic virus hemagglutinin shell (promoted the attachment of the virus to the cell) and neuraminidase (promotes penetration of the virus into the cell).
The reasons for the spread of swine flu
The mechanisms of infection:
- aerogenic (airborne path). Dangerous evolution of a patient sneezing, coughing – 1.5-2 meters in diameter;
- contact-household. Dangerous evolution of the patient on the hands of others, as well as household items (tables, surfaces, towels, cups) – the virus retains its properties for 2 hours or more (you can bring the virus from the hands to the oral mucosa and eyes).
Susceptibility to infections general. There are groups at risk of developing severe forms of swine flu:
- Children up to 5 years;
- Adults over 65 years old;
- pregnant women;
- Persons with underlying chronic diseases (chronic pulmonary diseases, oncology, blood disorders, liver disease, urinary system, heart, diabetes, and infectious immunodeficiencies such as HIV).
The source of infection – porcine (patients or virus carriers) and a sick man.
When a sick person becomes contagious?
One day before the onset of symptoms and during the week of the disease. A large epidemic have potential value in patients with end of the incubation period. Up to 15% of patients during treatment continue to excrete the virus for 10-14 days.
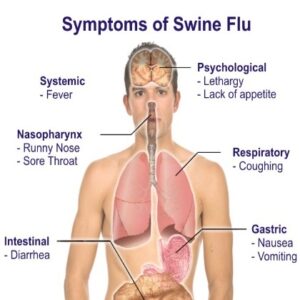
The symptoms of swine flu
The incubation period (from the time of infection until the first complaint) for swine flu lasts from days to 4 days, and sometimes extended to a week. Patients concerned about:
- Symptoms of intoxication, high temperature up to 38-39 °, marked weakness, muscle pain, nausea, vomiting of central origin, body aches, lethargy.
- Respiratory Syndrome: cough, expressed sore throat, feeling short of breath. The rapid development of one of the complications: the development of pneumonia in the early stages (2-3y day of illness).
The swine flu is different from ordinary flu?
The difference is the fact that 30-45% of patients with dyspeptic syndrome: persistent nausea, repeated vomiting, abnormal stools.
Swine flu H1N1: what is it?
In the early days of the disease: severe headaches, pain in the eyeballs, photophobia, which increases when moving eyes. Perhaps the development of serous meningitis, encephalitis. Muscle pain is an expression of symptoms.
One of the dangerous complications of swine flu is the development of pneumonia. Pneumonia may be the result of exposure to the influenza virus.
Primary pneumonia, especially
1. Developing the second or third day from the onset.
2. It is characterized by the development of symptoms of acute respiratory failure.
3. Appearance: the patient breathes (about 40 breaths per minute at a rate of – 16). The act of breathing actively involved supporting muscles (diaphragm, abdominal muscles).
4. Expressed dry or unproductive cough (mucous discharge and transparent).
5. dyspnea.
6. Turning blue skin (cyanosis).
7. crackles in the lower lung mainly at the height of inspiration, dullness in the light rapping.
Often primary pneumonia lead to the formation of respiratory lung edema with possible fatal outcome.
Secondary pneumonia, especially
1. There is a 6-10 day from the beginning of the disease.
2. Most often, there is a pneumococcal contamination (45% patients), at least Staphylococcus aureus (not more than 18%), and Haemophilus influenzae.
3. Increased cough: it becomes painful, almost constant.
4. The second wave of fever and intoxication.
5. The patient receives virtually no food.
6. increasing pain in the chest when coughing or even breathing.
7. Light emit yellow pus and mucus.
8. Radiography – foci of inflammation in the lung.
9. The flow of secondary pneumonia prolonged, patients can not recover a month and a half.
10. Often, staphylococcal pneumonia lead to the formation of lung abscess.
Mixed pneumonia
1. Clinical symptoms and audio, and a second pneumonia
2. is prolonged (progradiently), are difficult to treat.
Other complications of swine flu
Pericarditis, an infectious-allergic myocarditis, hemorrhagic syndrome.
When to see a doctor?
For children
– Rapid breathing, difficulty breathing movements;
– Bluish skin limbs and trunk;
– Waiver of eating and drinking;
– Repeated vomiting (vomiting “fountain”, as well as frequent regurgitation in infants – the equivalent of vomiting in this age);
– Apathy and lethargy of the child;
– Contrary agitation resistance, even when taking the child in his arms;
– The emergence of a second wave of symptoms with increased cough and shortness of breath.
For Adults
– Shortness of breath and increased it during the day;
– Pain in the chest when breathing or coughing;
– Severe dizziness, appearing suddenly;
– Periodically confusion (forgetfulness, loss of memory of specific events);
– Repeated vomiting and profuse;
– The second wave of fever, cough, shortness of breath.
It appears if the immune system?
Immunity after suffering flu: type-specific and short (1 year).
Diagnosis of swine flu
Preliminary diagnostics. Identify the probability of the disease:
– Contact with the flu, as well as the arrival of swine flu endemic areas (North America);
– Complaints of the patient on the gastrointestinal disorder in the background temperature and respiratory syndrome;
– Unexpressed or no sore throat amid strong mostly dry cough;
– Development of 2-3 hours with typical pneumonia symptoms (described above).
Final Diagnosis possible after laboratory confirmation of the disease:
– PCR diagnosis of nasopharyngeal mucus samples to detect RNA of influenza A (H1N1) CA / 2009;
– Virologic method of sowing nasopharyngeal mucus, sputum certain environment.
Treatment of swine flu H1N1 virus
1. compulsory hospitalization appointment of specific therapy.
2. Bed rest for a period of 5-7 days temperature and normal temperature.
3. Prevention of complications.
What to do if you suspect the disease?
If you notice symptoms of swine flu:
1. Stay at home, do not go to crowded places.
2. Houses around you to protect loved ones from infection – wear a mask and change it every 4 hours.
3. Call the doctor at home. If you come from endemic countries (Mexico, USA), tell your doctor.
4. Eat right: a diet with plenty of protein and a high content of vitamins A, C and Group B.
5. Acceptance of a sufficient amount of liquid (best fruit drinks of black currants, rose hips, chokeberry, lemon).
Admission antivirals (h1n1 virus)
Assign the following cases:
1. If the patient has one of these symptoms (fever, stuffy nose, cough, shortness of breath);
2. Dedicated laboratory influenza virus A / 2009 (H1N1);
3. The age group under 5 years;
4. Persons older – 65 years;
5. Pregnant women;
6 people with severe concomitant diseases and immunodeficiency;
Mild and moderate forms of swine flu allow the appointment of these antiviral drugs:
arbidol, interferon alfa-2b (Grippferon, viferon), interferon alfa-2a (IFN lipind) and gamma interferon (Ingaron) Ingavirin, Kagocel, tsikloferon.
If you have bacterial pneumonia character:
antibiotics (cephalosporins III-IV generation, carbapenems, fluoroquinolones Generation IV vancomycin).
Pathogenetic therapy includes detoxifying infusion therapy, corticosteroids, sympathomimetics to reduce the symptoms of intoxication, facilitate breathing (held in the hospital). At home, in the mild form of swine flu shows abundant drink (fruit drinks, tea, honey water).
Symptomatic treatment: antipyretic (paracetamol, ibuprofen), a nasal vasoconstrictor (nazol, tizin, nazivin, Otrivin and others), to relieve cough (Tussin, stoptussin, ambroxol, ACC and others), antihistamines (Claritin, zodak).
Particular attention is paid to children and pregnant women
Children: welcome aspirinsoderzhaschih banned drugs because of the risk of Reye’s syndrome (encephalopathy with edema of the brain and the development of liver failure), so preference is given paracetamol, nurofenu. Because antiviral agents are shown: Tamiflu, Relenza, viferon 1 Grippferon, reaferon lipind, Kagocel to 3 years, anaferon.
Pregnant women need to drink plenty of liquids, in the absence of edema;
– In mild forms – of antiviral drugs – viferon in candlelight Grippferon, arbidol, if you can not take tablets (vomiting) – intramuscular administration panavir; in severe forms of Tamiflu, Relenza, viferon;
– To reduce the severity of fever: paracetamol, Ascorutinum;
– The development of bacterial pneumonia: cephalosporins III-IV generation macrolides, carbapenems;
– During the epidemic is a mandatory hospitalization of all pregnant women with severe intoxication.
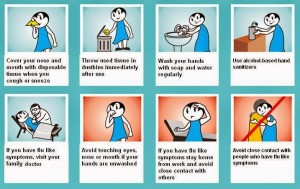
Prevention of swine flu (h1n1 virus)
Events for healthy (on WHO recommendations):
• Wash your hands often with soap and water, alcohol-containing solutions can be.
• Avoid close contact with sick people.
• Avoid hugs, kisses and handshakes.
• If you get sick, stay home and limit contact with others.
• If you have flu symptoms, seek immediate medical attention. If you are sick, stay home for 7 days after your symptoms in order to prevent infection of others.